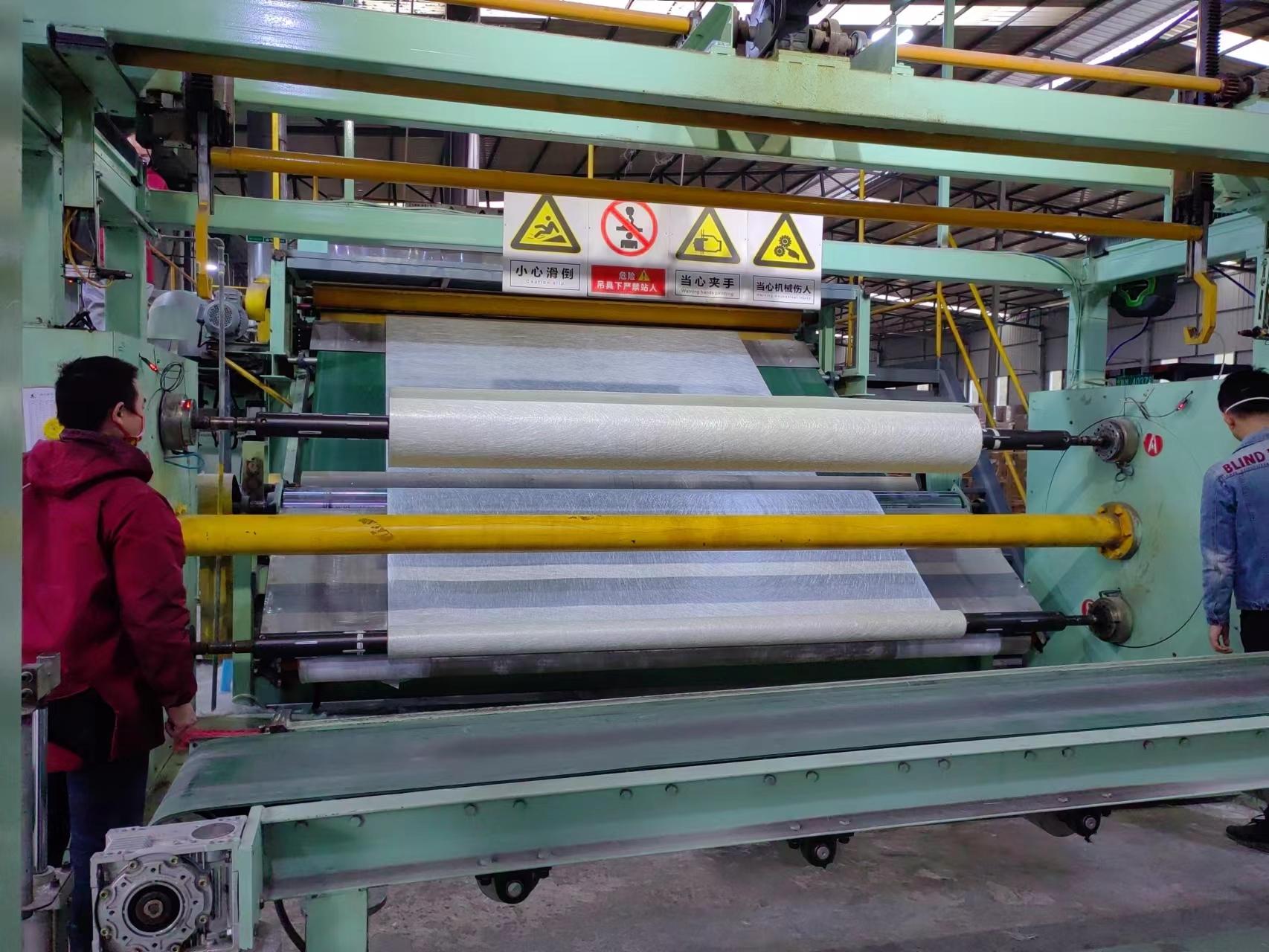
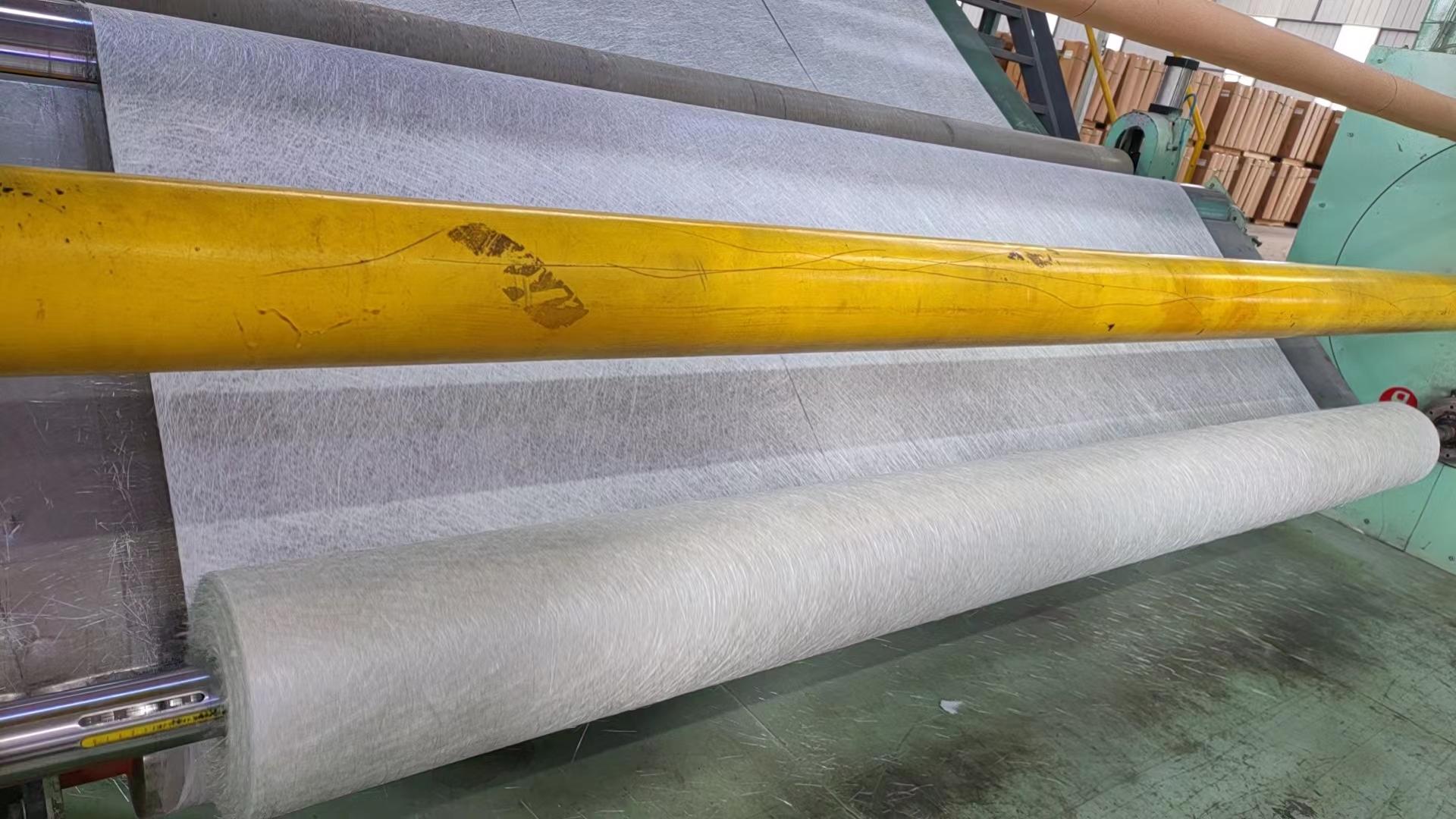
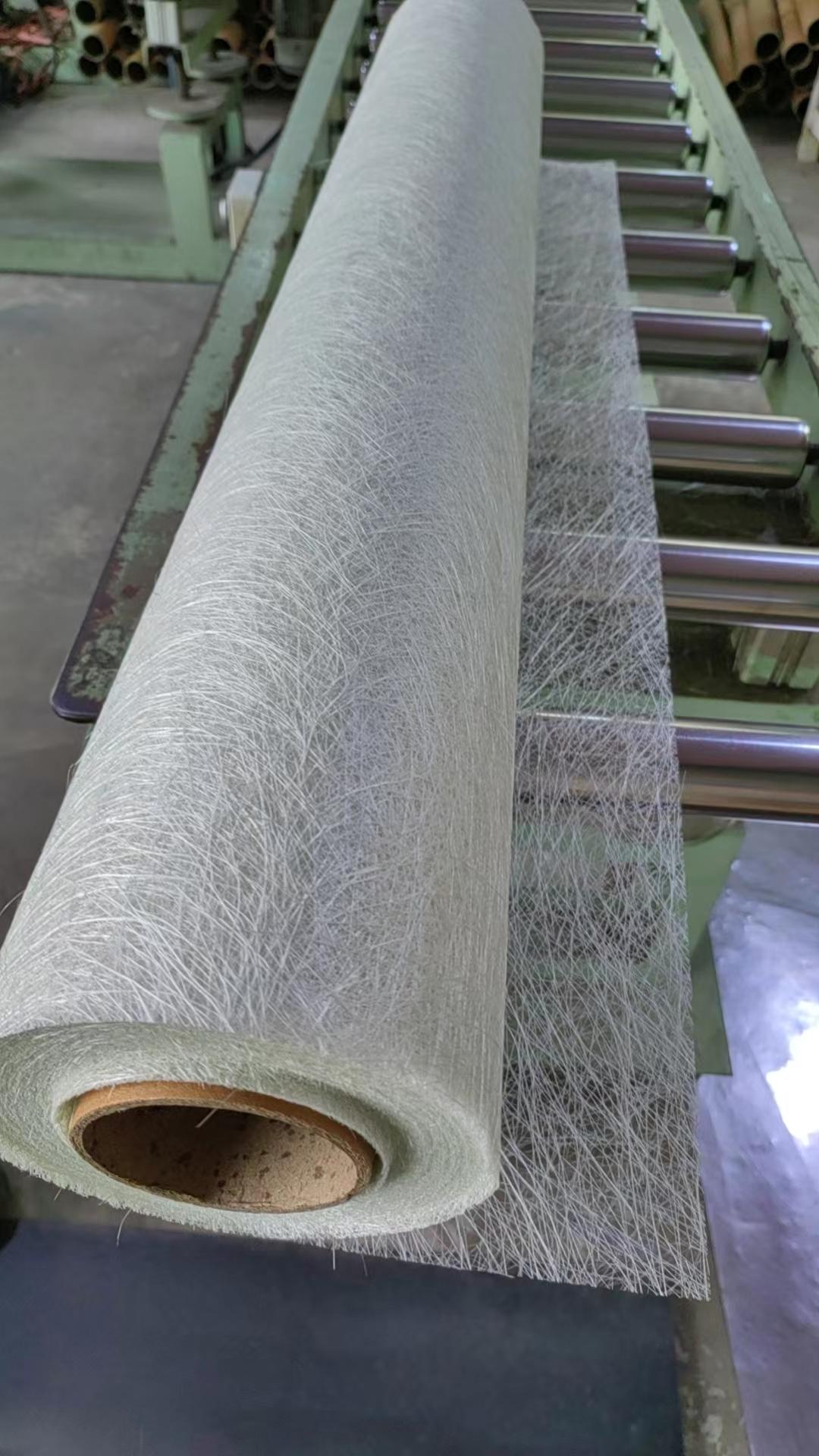
The use and function of glass fiber chopped strand mat
1. Composite material manufacturing
– Application scenarios: ship hulls, car bodies, wind turbine blades, storage tanks, pipelines, etc.
– Function: As a reinforcing material, it improves the strength, rigidity and impact resistance of the product after combining with resin while maintaining lightweight.
2. Construction field
– Application scenarios: roofs, wall panels, waterproof membranes, thermal insulation materials, etc.
– Function: Provide corrosion resistance and moisture resistance, enhance the durability of building materials, and simplify construction processes.
3. Anti-corrosion Engineering
– Application scenarios: chemical storage tanks, pipeline linings, pickling tanks, etc.
– Function: Using the acid and alkali resistance of glass fiber to protect equipment from chemical corrosion and extend service life.
4. Electronics and electrical
– Application scenarios: circuit substrates, insulation boards, electrical appliance housings, etc.
– Function: Provide excellent electrical insulation and high temperature resistance to ensure safe operation of equipment.
5. Transportation
– Application scenarios: aerospace components, rail transit bodies, new energy vehicle battery housings, etc.
– Function: Reduce structural weight, improve fuel efficiency or endurance, while maintaining high strength.
Core role
1. Enhanced performance: The random distribution of short-cut fibers gives the composite material isotropic strength, which is suitable for the molding of complex shapes.
2. Lightweight: Low density (about 2.5-2.7g/cm³), replacing metal can significantly reduce weight.
3. Corrosion resistance: Stable to media such as acids, alkalis, and salts, suitable for harsh environments.
4. Process adaptability: Compatible with processes such as hand lay-up, molding, and RTM (resin transfer molding), flexible processing.
5. Insulation and heat insulation: Non-conductive and low thermal conductivity, suitable for high temperature or electrical environments.